International Private Certifications Body for Entrepreneurs, Managers & CEOs Worldwide!
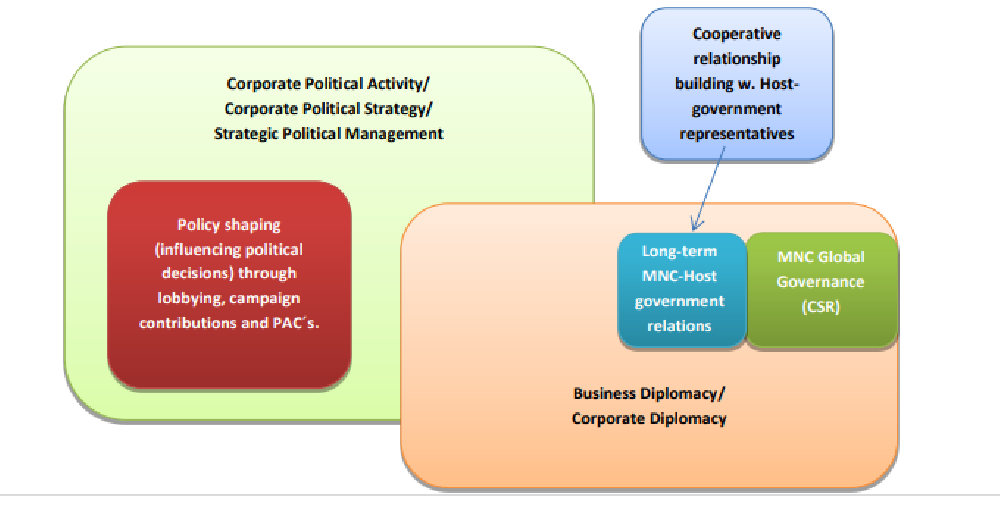
Business diplomacy intensity reflects the extent to which a company actively establishes and sustains positive relationships with foreign government representatives and non-governmental stakeholders. This dimension indicates how intensively the company executes business diplomacy. The second dimension, policy clarity, reflects the extent to which a MNC has a clear and organization-wide policy on how to establish and sustain these relationships. This dimension indicates whether there are formal/written rules for business diplomacy, or whether informal/unwritten guidelines exist. Business diplomacy breadth reflects the extent to which establishing and sustaining these relationships is done by every company representative. This dimension also indicates whether employees consider themselves as representatives of their organization when they are in contact with foreign government representatives and non-governmental stakeholders. As described in the literature review, London (1999) provides recommendations for making business diplomacy more effective in organizations. He suggests that managers should apply a diplomatic style of operation and that leaders should demonstrate the value of business diplomacy to peers, subordinates, customers, etc. Business diplomacy responsibility reflects the extent to which the company’s responsibility for establishing and sustaining positive relationships with foreign government representatives and non-governmental stakeholders lies on the headquarters level or with the foreign subsidiaries, or whether they are both jointly responsible. This dimension indicates whether business diplomacy is set by the headquarters for the whole organization (centralized), whether a Business diplomacy in multinational corporations: An exploratory study Ruël, Wolters, Loohuis 6 framework of guidelines is set by the headquarters within which a foreign subsidiary has some degree of freedom to act, or whether subsidiary executives are free to decide upon how to conduct business diplomacy (decentralized). The fifth dimension, means deployment, reflects the extent to which the company deploys a diversity of means for establishing and sustaining positive relationships with foreign government representatives and non-governmental stakeholders. It indicates which means, methods and channels (e.g. social meetings, public forums, seminars, local government debates, media channels, sponsor activities, etc.) are used by the firm for business diplomacy. Input for this dimension is derived from the scientific work of Luo (2001), and included in the literature review. He proposes four building blocks for improving a MNC’s cooperative relationships with host governments: political accommodation, resource complementarity, organizational credibility and personal relations. Business diplomacy resource availability reflects the extent to which the company uses multiple firm resources (e.g. financial, time, knowledge) to establish and sustain these relationships. Input for this dimension is partly derived from the work of Saner and Yiu (2005), and included in the literature review. They provide recommendations for how the CEO should be involved in providing all kinds of policy directives (e.g. a knowledge system for cumulative learning, business diplomacy training for middle managers, etc.) in order to make business diplomacy more effective.
https://www.diis.dk/files/media/publications/import/extra/business_diplomacy_in_mncs_-an_exploratory_study_final.pdf